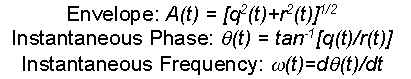What are Seismic Attributes?
"Seismic Attributes are all the information obtained from seismic data, either by direct measurements or by logical or experience based reasoning." (Taner, 2000)
Seismic attributes typically provide information relating to the amplitude, shape, and/or position of the seismic waveform.
Families of Attributes (based on method of generation)
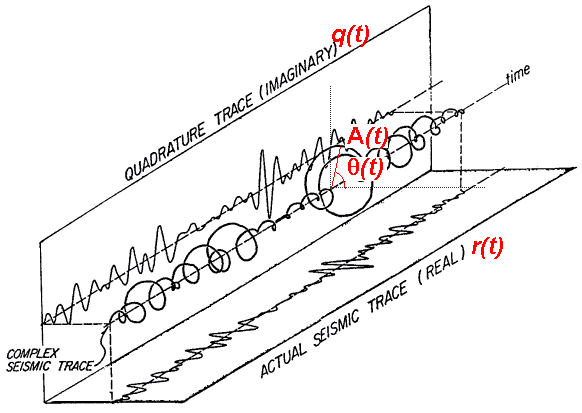
Complex Trace Attributes--The seismic data is treated as an analytic trace, which contains both real and imaginary parts. Various amplitude, phase, and frequency attributes can be calculated. Includes:
- Instantaneous Attributes--associated with a point in time
- Response Attributes--related to a lobe of the energy envelope A(t); corresponds to an event, rather than a single time sample
Figure 1. Complex Trace Attributes.
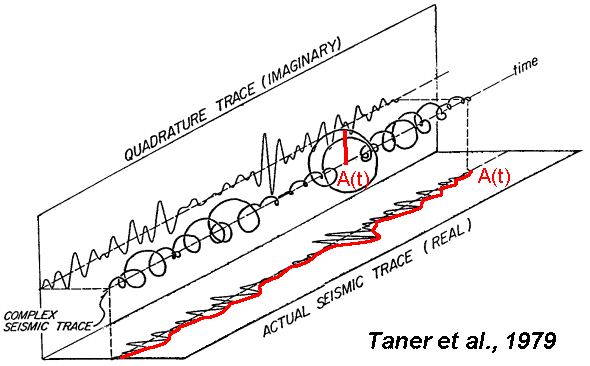
Fourier Attributes--frequency domain attributes obtained through Fourier analysis (e.g., amplitude variation with bandwidth in frequency (avbf), spectral decomposition)
Figure 2. Fourier Attributes.
Time Attributes--related to the vertical position of the waveform in the seismic section (e.g., horizon time picks, isochrons)
Window Attributes--attributes which summarize information from a vertical window of data.
Multi-trace Attributes--attributes calculated using more than one input seismic trace, which provide quantitative information about lateral variations in the seismic data (e.g., coherence, dip/azimuth)
| Some representative seismic attributes |
|---|
Instantaneous Attributes
- Envelope
- Instantaneous Phase
- Instantaneous Frequency
- Weighted Average Frequency
- Apparent Polarity
Response Attributes
- Response Amplitude
- Response Phase
- Response Frequency
- Response Length
- Skewness
- Rise Time
Frequency Attributes
- avbf
- Spectral Decomposition
|
Window Attributes
- Maximum Absolute Amplitude
- Time of Maximum Absolute Amplitude
- Average Absolute Amplitude
- Sum of Absolute Amplitudes
- Average Instantaneous Frequency
- Number of Zero Crossings
- Largest Peak/Trough Amplitude Difference
- Largest Peak/Trough Time Difference
Multi-trace Attributes
|
Definitions of selected attributes
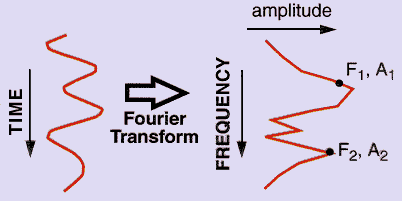
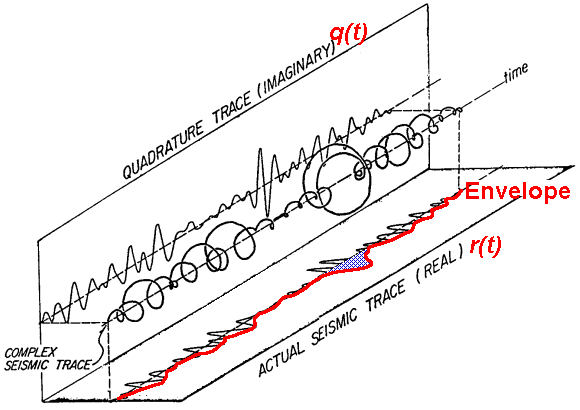
Instantaneous Attributes
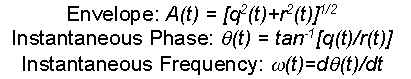
Figure 3. Instantaneous Attributes.
Response Attributes of shaded area
Response Amplitude: maximum envelope
Response Phase: value of instantaneous phase at time of maximum envelope
Response Frequency: value of instantaneous frequency at time of maximum envelope
Figure 4. Response Attributes of shaded area.
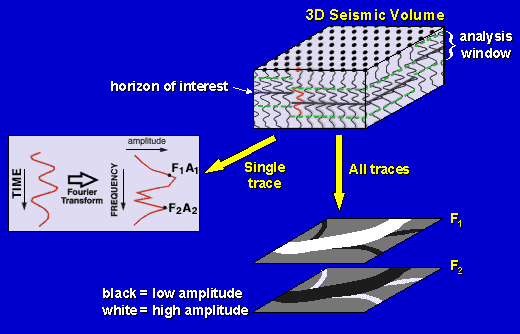
Spectral Decomposition
Uses the Fourier transform to calculate the amplitude spectrum of a short time window covering the zone of interest.
The amplitude spectrum is tuned by the geologic units within the analysis window, so that units with different rock properties and/or thickness will exhibit different amplitude responses.
Figure 5. Spectral Decomposition.
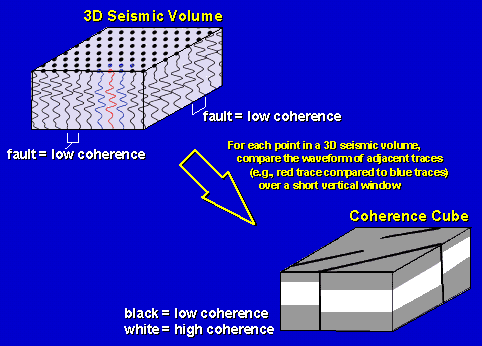
Seismic Coherence
Seismic Coherence is a measure of the trace-to-trace similarity of the seismic waveform within a small analysis window.
Figure 6. Seismic Coherence.
What physical information is provided by these attributes?
Envelope--presence of gas (bright spots), thin-bed tuning effects, lithology changes
Phase--lateral continuity of reflectors, bedding configurations
Frequency--bed thickness, presence of hydrocarbons, fracture zones
Spectral Decomposition--bed thickness
Coherence--faults, fractures, lateral stratigraphic discontinuities
How can I generate attributes?
Most workstation-based seismic interpretation systems have tools for generating a suite of complex trace attributes. The KINGDOM Suite, a PC-based interpretation system from Seismic Micro-Technology, Inc., was used to generate the attributes for this presentation.
Spectral decomposition is a part of the OpenSEIS processing system, available for Unix and Linux platforms from OpenGeoSolutions.
Coherence CubeTM processing can be obtained from Scott Pickford. There are also several software products available which calculate coherence-type attributes (e.g., Variance Cube fromGeoQuest or PostStack ESP from Landmark).
Methods of interpreting attributes
Identify spatial patterns/trends in attribute data
- Cross-sectional view
- Map view (attributes extracted along horizon or from zone of interest)
- 3D visualization
Tie attributes to well control using statistical methods (e.g., crossplots)
Automatically analyze multiple attributes (with or without well control)
- Geostatistics
- Principal component analysis
- Cluster analysis
- Texture analysis
Next Page--Example--"D" Sand, Sooner Unit, Colorado
Kansas Geological Survey
Send comments and/or suggestions to webadmin@kgs.ku.edu
Updated Nov. 25, 2002
URL = http://www.kgs.ku.edu/PRS/publication/2002/ofr49/index.html
|