
PfEFFER Version 2.0
(Petrofacies Evaluation of Formations for Engineering Reservoirs)
Previous Page--PfEFFER Home ||
Next Page--New Features
Synopsis of PfEFFER features
The minimum log data required by the spreadsheet-based software are a
porosity and resistivity log. Old logs are well suited to this analysis
once they are digitized or simply typed into the spreadsheet. Toolbars
and menus perform most operations through the utilization of nearly
8,000 lines of Visual Basic code. PfEFFER v. 1 reads standard LAS log
data files such as those obtained from a logging truck or permits manual
entry, organizes digital data by well and zone, and creates a "Super
Pickett" crossplot, depth plots, and lithology solutions (if sufficient
logs are available).
The software is focused on interpreting and analyzing reservoir pore
type, permeability trends, and variations in mineral composition.
PfEFFER v. 1 provides procedures for optimal estimation of bulk volume
water and water saturation (including irreducible values) to better
evaluate potential production, reservoir quality, and heterogeneity.
Also capillary pressure data can be incorporated to further calibrate
well log data with pore size or to assess depth to the free water level.
The program will assemble zonal information from well workbooks into a
project workbook and can automatically generate map and 3-D
visualizations of key parameters as defined by the user. "Hot links"
are maintained in the project workbook to each well workbook to aid in
data management.
In addition to revising the appearance of the spreadsheet and refining the
modules as described above, PfEFFER v. 2.0 contains new modules including pay
flag cutoffs, a flow unit column, depth-constrained cluster analysis, moveable
oil plots and calculations, shaly log analysis, Hough transform for simultaneous
solution of Archie equation constants and formation water resistivity, secondary
porosity, and petrophysical forward modeling.
Three additional modules (add-ins) are available as PfEFFER Pro. These modules
include color cross section generation, map coordinate conversion
(longitude-latitude to UTM x-y), and software to help build an input file for a
reservoir simulator based on the petrophysical characterization. DOE's freeware
reservoir simulation software, BOAST 3, was used in the development and testing.
All of the standard EXCEL features continue to be available to users for
independent analysis and data exploration. The simplicity of hardware and
software requirements means that PfEFFER is an attractive option for companies of
all sizes. The range and versatility of module capabilities makes them powerful
tools for the analysis of both old log suites and the latest generation of
logging measurements.
Reads log ASCII standard (LAS) digitial files, establishes new
worksheets including header information, reads specified depth intervals, names
zone, and appends new log data to old workbook.
Log Display
Depth-related information can be displayed as vertical depth EXCEL
charts. Log traces can be combined on a single chart. Standard EXCEL
features permit stretching the log(s) to change image size; scales;
annotation of logs; and size adjustment, type, and color of the log
traces. Charts can be printed separately or grouped and cut and pasted
into other Windows applications, e.g., building cross sections.
Calculation of Porosity
Porosity can be calculated using density, neutron, density/neutron, or
sonic with and without correction for shale volume. Secondary porosity
can also be calculated.
"Super Pickett" Crossplot
The focal point of the analytical routines and graphical displays is the
"Super
Pickett" crossplot, an extension of the standard log-log
porosity/resistivity
plot. The special features in this crossplot include:
- tracking the pattern of data points by depth,
- annotation of the crossplot with bulk volume water and permeability
lines in addition to the standard water saturation lines.
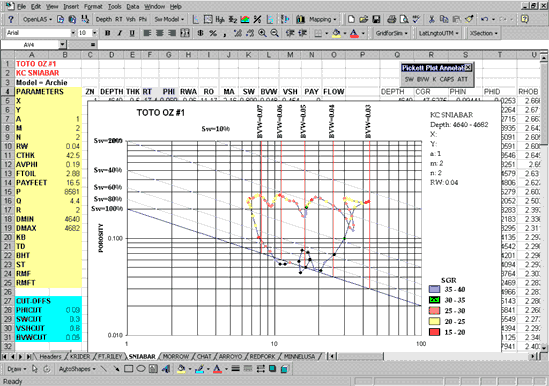
Distinctive depth-related trends and patterns on the crossplots have been
recognized from hundreds of examples, initially "fingerprinting" an individual
reservoir, tracking subtle variations among sets of wells in the same reservoir,
and comparing stacked reservoirs. Specific parameters obtained from the
crossplots include minimum bulk volume water and associated porosity and water
saturations, permeability estimates, resistivity gradients reflecting hydrocarbon
transition zones and depth of possible free water levels, and reservoir
zonation/permeability barriers and associated heterogeneities. Comparisons of
crossplots in the same reservoir among several wells can be used to evaluate
reservoir connectedness (conformance).
Color is used in the data shown on the "Super Pickett" crossplot to display
attributes such as well log data, completion information, and other derived data
described below. Color ranges are automatically or manually selected to
highlight and emphasize reservoir components, adding new perspectives to the
reservoir.
Shaly Sand Models for Sw Calculation
Sw model menu permits selection of Archie water-saturation model (the
default) and two shaly sand modeld, the Simandoux model and the
Dual-Water model.
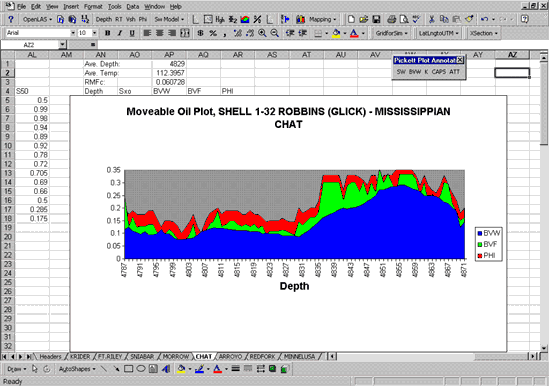
Moveable Hydrocarbon
Based on the assumption that the zone near the well is permeated with
mud filtrate, the Archie equation is used to compute Sxo, the filtrate
saturation of this flushed zone. Sxo is used to compute moveable and
residual hydrocarbon saturations. PfEFFER generates a moveable oil plot
consisting of bulk volume water, bulk volume fluid, and porosity.
Difference between BVF and BVW represents the moveable hydrocarbons
saturation.
Pay-flag Cutoffs
Button can be activated to add color to cells of selected variables used
to determine pay including porosity, BVW, Sw, and/or Vsh. A pay column
reveals computed fractional hydrocarbon volumnes based on cutoff
selection.
Lithological Analysis
Includes two options in PfEFFER v. 2.0, one based on the RHOMAA-UMAA
plot and the other allowing a more general selection of logs and system
components. The general option allows the user to compute up to six
components based on up to five logs. Any log can be employed and the
component selection is at the discretion of the user.
Capillary Pressure
The "CAP" module overlays capillary pressure curves as contoured surfaces on
the "Super Pickett" crossplot. The overlay utilizes capillary pressure data from
samples analyzed from the reservoir (presented as water saturation and porosity
vs. capillary pressure for various pore types). The resulting capillary pressure
contours can serve as templates in the distinction of separate pore-type
petrofacies, determination of pore-throat sizes, and prediction of elevation
above free-water level, when integrated with digital log data.
Zonation by Depth-constrained Cluster Analysis
Analysis can be employed to segment the entire spreadsheet into
subintervals based on a user-specified set of logs. A heirarchical
cluster (Ward's method) is used to produce subintervals that are as
homogeneous as possible and distinct as possible from each other, in
terms of their log characteristics. With output including columns of
class membership and average log values in these classes, the option is
useful in designating flow units and can be used as a quick and simple
blocking function.
Forward Modeling
Implements equations developed by Pittman to predict values of rx
(radius of smallest pore-throat), capillary pressure, and hydrocarbon
column height for a range of water-saturation values based on specific
values of permeability and porosity.
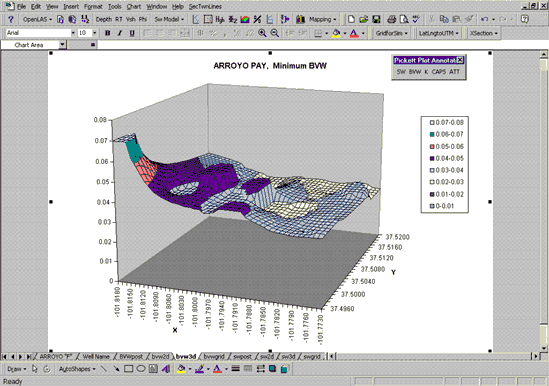
Mapping
The Mapping module produces a "first-look" map to examine spatial
variability/continuity among wells, assess reservoir heterogeneity, and evaluate
the consistency of the variables being mapped. A commercial mapping package is
needed if a more complete spatial analysis is desired. PfEFFER plot files can be
easily exported to most mapping programs using standard features of EXCEL.
The "mapping" or project workbook is electronically linked to "well" workbooks
and associated "reservoir" worksheets. Information changed in a reservoir
worksheet level is reflected in the mapping workbook. Griding, base map
generation, 2-D and 3-D visualization of the parameters are accomplished
automatically as selections from the mapping menu. A series of dialog boxes lead
the user through assembling wells, reservoirs, and defining mapping parameters.
Previous Page--PfEFFER Home ||
Next Page--New Features
Kansas Geological Survey, PfEFFER software
Comments to webadmin@kgs.ku.edu
Updated August 7, 1998
URL = http://www.kgs.ku.edu/PRS/software/pfeffer2.html
