

Kansas Geological Survey, Public Information Circular (PIC) 1
A User's Guide to Well-spacing Requirements for
the Dakota Aquifer in Kansas--Part 3 of 5
Sources of Freshwater Recharge for the Dakota Aquifer
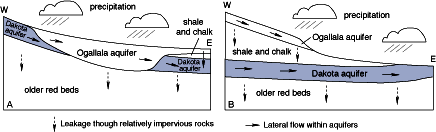
Figure 1 illustrates the areal extent of the Dakota
aquifer in Kansas. At its eastern extent in central Kansas, the Dakota is a
shallow aquifer that is at or near the surface. In this area, precipitation
enters the aquifer directly, adding recharge (replenishment of the aquifer with
water, usually a direct or indirect result of precipitation). In parts of
southwestern and south-central Kansas, the Dakota aquifer is directly beneath
the water-saturated Ogallala aquifer (figure 4A). Research shows that both
aquifers behaved largely as a single system prior to water-well development.
Near the Kansas-Colorado border in areas unaffected by pumping, the Dakota
aquifer recharges the Ogallala aquifer, but farther to the east, the Ogallala
recharges the Dakota. In northwestern Kansas, the Dakota aquifer is overlain
by a sequence of relatively impervious shales and chalks that are up to 2,000
feet (600 m) thick in the northwest corner of the state. Recharge from
precipitation in this part of the aquifer is negligible, except where this
impervious layer is very thin near its eastern and southern extents (figure 4B).
Figure 4--Ground-water flow. Diagrams not to scale.
New Well-spacing Requirements for the Dakota Aquifer in Kansas
In 1994, the Division of Water Resources of the Kansas Department of
Agriculture, the State agency that regulates water-well development,
modified the existing well-spacing requirements for the Dakota aquifer
based on research results from the Dakota Aquifer Program. Well-spacing
requirements are based on the aquifer's recharge capabilities and flow
rates.
- Where the Dakota aquifer is at the surface or beneath the Ogallala aquifer (generally areas of rapid recharge), the new-well spacing is 0.5
mile (0.8 km) for all wells other than domestic, and 1,320 feet (396 m) for domestic wells.
- The new-well spacing where the Dakota aquifer is overlain by impervious rock units (generally very slow recharge) is 4 miles (6.4 km)
for all wells other than domestic, and 0.5 mile (0.8 km) for domestic wells.
Kansas Geological Survey, Geology Extension
Web version Nov. 1995
http://www.kgs.ku.edu/Publications/pic1/pic1_3.html